|
Article ID: 55
Last updated: 09 Sep, 2019
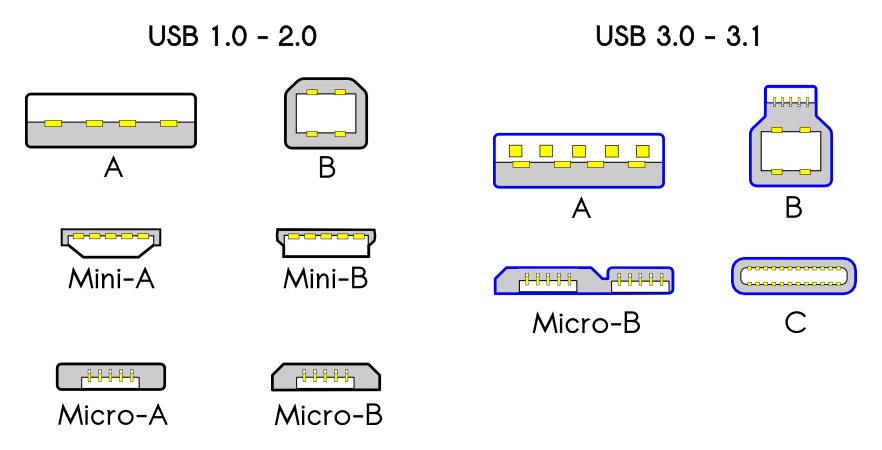
A Brief Look At: USB Type-C™What is it?USB Type-C™ is the new USB plug and port connection developed by the USB Implementers’ Forum (USB-IF) which is the governing body for USB technology. It seeks to replace the USB Type-A and USB Type-B found on most computing devices with a versatile, smaller, and reversible connection. The underlying technology of this new connection is designed to support faster data transfer rates (up to 20Gbps), more charging power (up to 100W), and video / audio capability through alternate mode. USB Type-C can support alternate display protocols such as DisplayPort™, Thunderbolt™ 3, and MHL™. Devices that will support USB Type-C range from notebooks and smartphones to external Hard Drives and audio equipment. The shift in technology is in part motivated by the preference for devices to be more compact yet more capable then they have previously been, a capability not easily achieved with a technology that is over 16 years old. Types of USB ConnectorsUSB connector types multiplied as the specification progressed. The original USB specification detailed Type-A and Type-B plugs and receptacles. The USB Type-C Specification defines a new small reversible-plug connector for USB devices. The Type-C plug connects to both hosts and devices, replacing various Type-A and Type-B connectors and cables [1].
Image Credit: Wikipedia Transfer RatesWhile USB transfer rate capabilities are a core feature to this technology, USB Type-C and USB 3.1 are not synonymous. Essentially, USB Type C refers to the reversible connection type, while the version numbers refer the data transfer speeds and other specs that a port or cable supports [2]. USB Type-C does not necessarily come with USB 3.1 Gen 2 speed. Many smartphones and tablets have USB-C 2.0, which is mainly for low speed data and charging. USB 3.1 Gen 2 speed also does not has to be through USB Type-C. USB Type-A and USB Type-B can also deliver up to 10Gbpes USB 3.1 Gen 2 speed. What happened to USB 3.0? The USB-IF has renamed this specification USB 3.1 Gen 1 with the implementation of Type-C. Not all USB-C cables or devices are capable of supporting USB 3.1 Gen 2 speed. Always consult the specifications for your devices to confirm support for the maximum speed. USB-IF also announced the publication of USB 4 specification, which will increase the maximum bandwidth to 40Gbps making it one of the fastest ports available on a computer.
Power DeliveryThe addition of the power delivery capability to USB Type-C effectively reduces the clutter of having to carry multiple cables and adapters for power, A/V, and data transfer. This additional specification allows for a theoretical 100W max charging power, which is sufficient to charge devices larger than tablets such as laptops. Power Delivery is in its infancy but will become more widely adopted as device manufactures and connectivity providers develop the technology. Not all USB-C cables or devices are capable of supporting USB PD. Always consult the specifications for your devices to confirm support for the PD (as well as the maxium charging power). Table 2-1 USB Type-C Specification Release 1.3
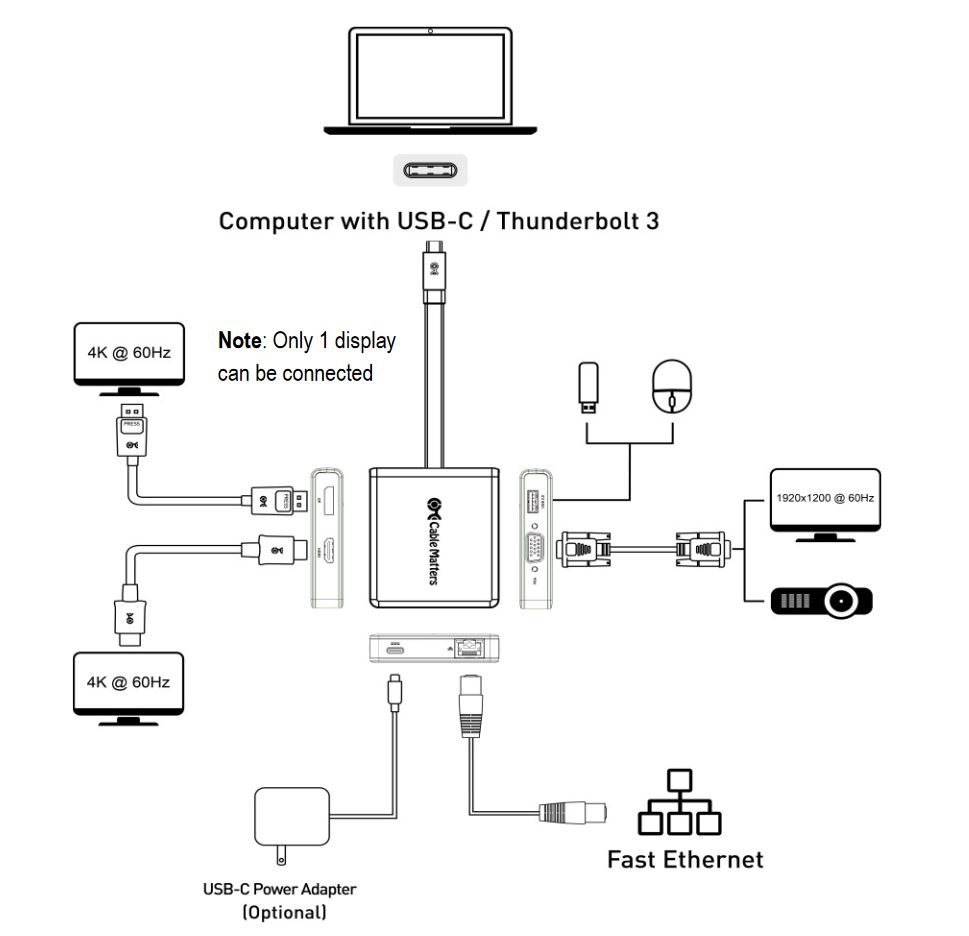
Alternate ModesFor the first time, the USB-IF has allowed alternate protocols on their connectors to extend the capabilities of this connection. The addition of non-USB formats like DisplayPort, Thunderbolt 3, and MHL will allow devices to connect to displays and transfer data at higher speeds through a single USB-C cable. For example, Thunderbolt 3 can allow for bandwidth up to 40Gbps and support dual 4k displays @ 60Hz. This allows for ultra-fast data transfer to and from a Hard Drive or support for the latest TVs and monitors all in a compact adapter. Not all USB Type-C cables or devices are capable of supporting these technologies. Always consult the specifications for your devices to confirm support for alternate modes. As an example, some laptops support Type-C but do not support Thunderbolt 3 or alternate modes. Computers and smartphones with USB-C 2.0 will not support alternate modes and thus, are not capable of transmitting video. Form FactorWith the evolution of devices using Type-C technology, many electronics will have fewer connectivity ports, becoming slimmer and more portable while remaining just as powerful. In fact, Apple has done just that on their 12” Apple MacBook, which features only a single Type-C port and is 24% thinner and 15% lighter than the 11” MacBook Air. This reduction of connectivity options means that adapters will become more important accessories. For example, a laptop equipped with a single Type-C port will require a user to have an adapter to connect an HDMI equipped monitor or a USB hub for standard USB devices like hard drives and printers. Currently, Cable Matters has several connectivity solutions for Type-C devices and is continuously adding more.
What’s the difference between Cable Matters Type-C/Thunderbolt 3 products and other brands?The USB-IF provides the requirements for manufacturers to follow, however it is the responsibility of those brands to ensure consistent performance of their products and to properly support them. As a member of the USB-IF we ensure that our Product Research and Development Team diligently tests compatibility with a broad range of devices so our Type-C products perform as advertised. Cable Matters is among a limited group of manufacturers to officially support Thunderbolt 3 technology. Combined with strict quality control and supported by a responsive customer service team, Cable Matters is the clear choice for your Type-C/Thunderbolt 3 connectivity solutions. Need help deciding which USB C cable to buy?Contact us here. Cable Matters will help you navigate the confusing choices of USB-C data and charging cable types. We will provide you with the best solution to maximize the capabilities of your equipment and ensure compatibility. Sources & Disclaimers: 1. USB (Physical) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/USB_(Physical)#Connectors 2. USB Type C and 3.1: clearing up the confusion https://www.androidauthority.com/usb-type-c-and-3-1-explained-656552/ 3. Table 2-1, USB Type-C Specification RElease 1.3 (PDF) p. 26 Apple MacBook, apple.com; Apple, MacBook, MacBook are trademarks of Apple Inc. Thunderbolt and the Thunderbolt logo are trademarks of the Intel Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries USB Type-C™ and USB-C™ are trademarks of the USB Implementers Forum.
Article ID: 55
Last updated: 09 Sep, 2019
Revision: 23
Tags
|